Two names have become a synonym for web security, the SSL Certificate and the Code Signing Certificate. Although both are digital certificates that use the same X.509 Public Key Infrastructure(PKI), they offer security solutions that can not be swapped. In addition, both require verification of the buyer from the Certificate Authority(CA) before certificates are issued to them.
At the user end, it can sometimes be confusing which one will serve your purpose. The certificates trigger security warnings if the SSL Certificate or the Code Signing Certificate is not installed. Hence, it becomes impervious to know the critical differences between them. But before that, let us try to understand the very basics.
Understanding SSL Certificate
SSL Certificate is a digital certificate issued to a website that encrypts all the information exchanged between the user web browser and the client-server. This encryption protects the website against data theft by, say, Man-in-the-middle attacks and authenticates the webserver.
After the SSL Certificate is installed on the server, the website’s protocol changes from HTTP to secured HTTPS, and as a visual symbol of trust, a padlock is introduced before the URL of the website. You can click on this padlock to view the details of the SSL Certificate as validity etc., as shown in the example below.
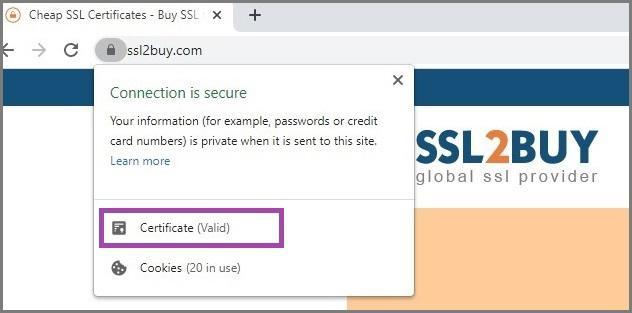
On the other hand, if the SSL Certificate does not secure the site, Google gives a shout-out warning to the user against the insecure website, as shown in the image below.
Code Signing Certificate Basics
A code signing certificate is a digital certificate issued by CA to a publisher or a software developer to authenticate their software or code.
It also ensures the integrity of the code-signed software and prevents any malicious code tampering. Code signing essentially involves a digital signature applied to the code by hashing it with the software.
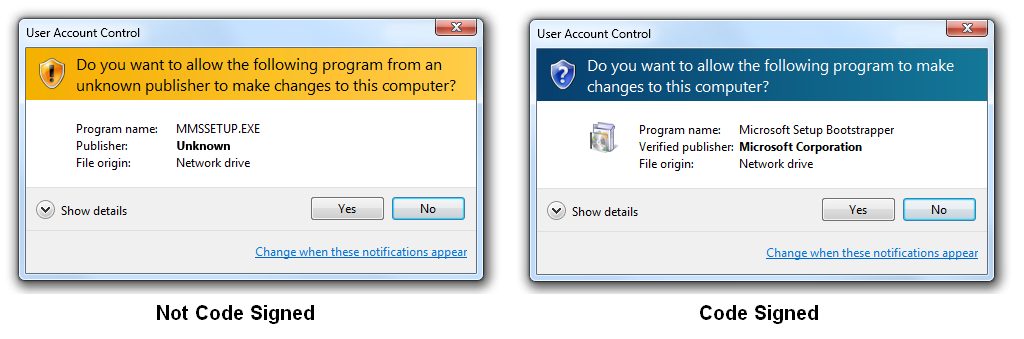
A warning message is initiated without a Code signing certificate when any malicious code or software sourced from an unknown publisher is initiated. One such example is shown in the image below.
Research well and be aware of your functional requirements, budgets and align your investment on the Code signing certificate accordingly. Say, e.g. investing in a very high-end certificate offered by a most reputed provider that comes with a hefty price tag could instead be replaced with a cheap code signing certificate that comes bundled with some beneficial perks and gives you a better value for money, not to mention the same encryption level.
Now that we have clear concepts of the two certificates let us focus on the key differences: Code signing and SSL certificates.
Application
An SSL Certificate finds application in providing security to the websites. So, an SSL certificate is used by website owners.
A Code Signing Certificate finds applications in protecting software or code integrity. Hence, Code Signing Certificate is used by software developers. But, if you are involved in developing your software and distributing it through your website, you may need both an SSL Certificate and a Code Signing Certificate.
Check Authentication Details
Once the website is SSL Certificate secured, a visual symbol of trust, a padlock is prefixed to the URL of the website. When you click on this padlock, you can view the SSL Certificate and its details like name of the issuing CA, domain name to which certificate has been issued, issuing date, expiry date, validity, etc., as discussed above in the basics of SSL Certificate. This gives assurance to the visitors that they are visiting an authentic site.
After going through the entire vetting process for the Code Signing Certificate, the developer’s digital signature is attached to the software. So when the user downloads the software, they can see the verified developer’s name. We have seen this in the example above, that of the basics of Code Signing Certificate. The user feels assured that the product they are downloading is safe and a genuine one.
Identity Attestation
Both SSL Certificate and Code Signing Certificate are issued to the buyer only after being attested by the Certificate Authority(CA). In the case of an SSL Certificate, the CA will verify your domain ownership for which Domain Validated(DV) SSL Certificate has been applied. This is done by a short process of sending an email to a specified email address with a verification link. However, in the cases of Organization Validation or Extended Validation(EV), SSL Certificates a much stringent and more prolonged verification procedure is carried out, and the CA will verify your business registration document, physical address, and phone number, etc.
The CA attestation procedure involves submitting a notarized form that authenticates your government-issued photo identification for individual software developers. Then you will be required to complete a phone call verification.
Pricing Of SSL Certificate and Code Signing Certificate
The pricing for a basic level Domain Validated(DV)SSL Certificate starts from somewhere near $8-$10 per year to pricing starting from $48/year for the Organization Validated(OV)SSL Certificate and around $60- $90/year for Extended Validated(EV)SSL Certificate.
For an OV Code Signing Certificate, you will have to pay the price starting from $80/year and the EV Code Signing Certificate starting from $300/year.
Certificate Expiration
Once the SSL Certificate validity period expires, a ‘not secure’ warning is triggered upon a user’s visit to your website, and it needs to be renewed.
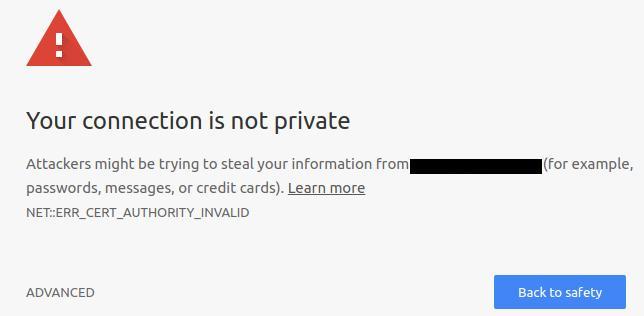
The Code Signing Certificate also triggers an ‘unknown/unverified publisher’ warning if the certificate has expired. The certificate must be renewed to stop showing this warning unless the Code signing Certificate uses time stamping.
With time stamping, the developer’s name is still visible. However, the certificate has expired, and users can be assured that you are the verified original publisher of the code and that it was signed when the certificate was valid.
Warranties Offered
Paid SSL Certificates carry warranties starting from $10,000 upwards, depending on the type of SSL Certificate you purchase. Warranties are worth paying attention to when investing in an SSL Certificate for your business, as the CA offering good warranty amounts can be an excellent support to any unseen future unfortunate incident of mis-issuance.
Code signing certificates usually do not carry any warranties, but a few reputed CAs like Thawte Brand usually offer a $50,000 warranty for Code signing certificates.
In conclusion:
We can say that although both SSL Certificate and Code Signing Certificate provide the highest level of security and help you gain user’s trust, they have entirely different applications. The SSL Certificate for securing websites and Code Signing Certificates for securing downloadable software.












