Stem cell therapies as regenerative medicine are a breakthrough for treating untreatable neurodegenerative diseases like autism. When combined with other interventions, stem cell therapy for autism effectively mitigates the symptoms and substantially improves the quality of life.
Stem cell therapy is an intriguing treatment approach for neurodiverse autistic children, with the ability to minimize behavioral issues long-term. Research involving stem cells and autism has shown positive results in improving the overall regulation of the immune system and neural connectivity underlying the condition.
Let’s dive deeper into what autism is and take a look at the research that supports stem cells as one of the most promising treatments for autistic individuals.
Autism may be the result of inflammation in the brain or miswiring
Research and evidence support autism to be linked to neuroinflammation and immune dysfunction. More than 10 years of studies have proven that a large subset of neurodiverse individuals suffers from chronic microglia activation within their brains, leading to inflammation or miswiring.
Another piece of evidence supported by research indicates that immune dysregulation in autism leads to inflammation, cytokine dysregulation, and anti-brain antibodies, which largely influence the onset of autism spectrum disorder at an early age.
What are the signs of autism?
In autism, both immune dysfunction and brain inflammation can lead to brain miswiring, causing symptoms like:
- Behavioral dysfunctions
- Lack of social skills
- Intellectual disabilities
Unfortunately, there`s no answer to how autism is diagnosed. No blood test can detect the presence of this neurodegenerative disorder at any stage. Autism can only be diagnosed at a later stage when behavioral, social, and intellectual limitations are observable.
According to experts, early diagnosis and interventions can prevent the illness from worsening and improve symptom management. Therefore, the stage of the disorder also has a significant impact on how well stem cell therapy and interventions work for a particular individual.
Stem cell medicine is a positive treatment
Stem cells due to their immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties are considered one of the best available treatments for autism spectrum disorder. Stem cell differentiation into specialized cells helps regenerate, repair, and replace damaged or unhealthy cells with healthy ones.
When combined with other interventions, stem cell therapy for autism can produce long-lasting results and remarkable improvements in:
- Reducing aggressive behaviors and hyperactivity
- Improved visual contact and attention span
- Enhanced social and communication skills
How stem cells target damaged areas
Stem cells prior to differentiation can be found as raw materials within the body. These cells under the right conditions have the ability to divide into two cells called daughter cells. These daughter cells then either transform into new stem cells or specialized cells, for instance, blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells, or bone cells.
Stem cells have a unique intrinsic tendency to target inflammations within the body and repair damaged cells and tissues. Once injected into the body or special organ, they can regenerate the damaged brain tissues, reduce inflammation, and modulate the immune system for improved health, and standard of life.
Stem cell therapy can be administered intravenously, intrathecally, or injected directly into problem areas depending upon the treatment requirements.
Research and treatment today focus on different types of stem cells
Stem cells have 4 types and not all stem cells are alike or produce desired results under the same circumstances.
Types of stem cells include:
- Embryonic stem cells.
- Tissue-specific stem cells or adult stem cells.
- Mesenchymal stem cells.
- Induced pluripotent stem cells.
Embryonic stem cells
These cells are derived from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst. They are pluripotent, meaning they have the capability of developing into any specialized body cells besides the placenta and umbilical cord.
Tissue-specific/ Adult stem cells
Adult stem cells can be found throughout the body, for instance, skin, blood, and gut. These cells are far more specialized than embryonic stem cells, with the ability into differentiating into any cell or tissue type they are injected into.
Mesenchymal stem cells
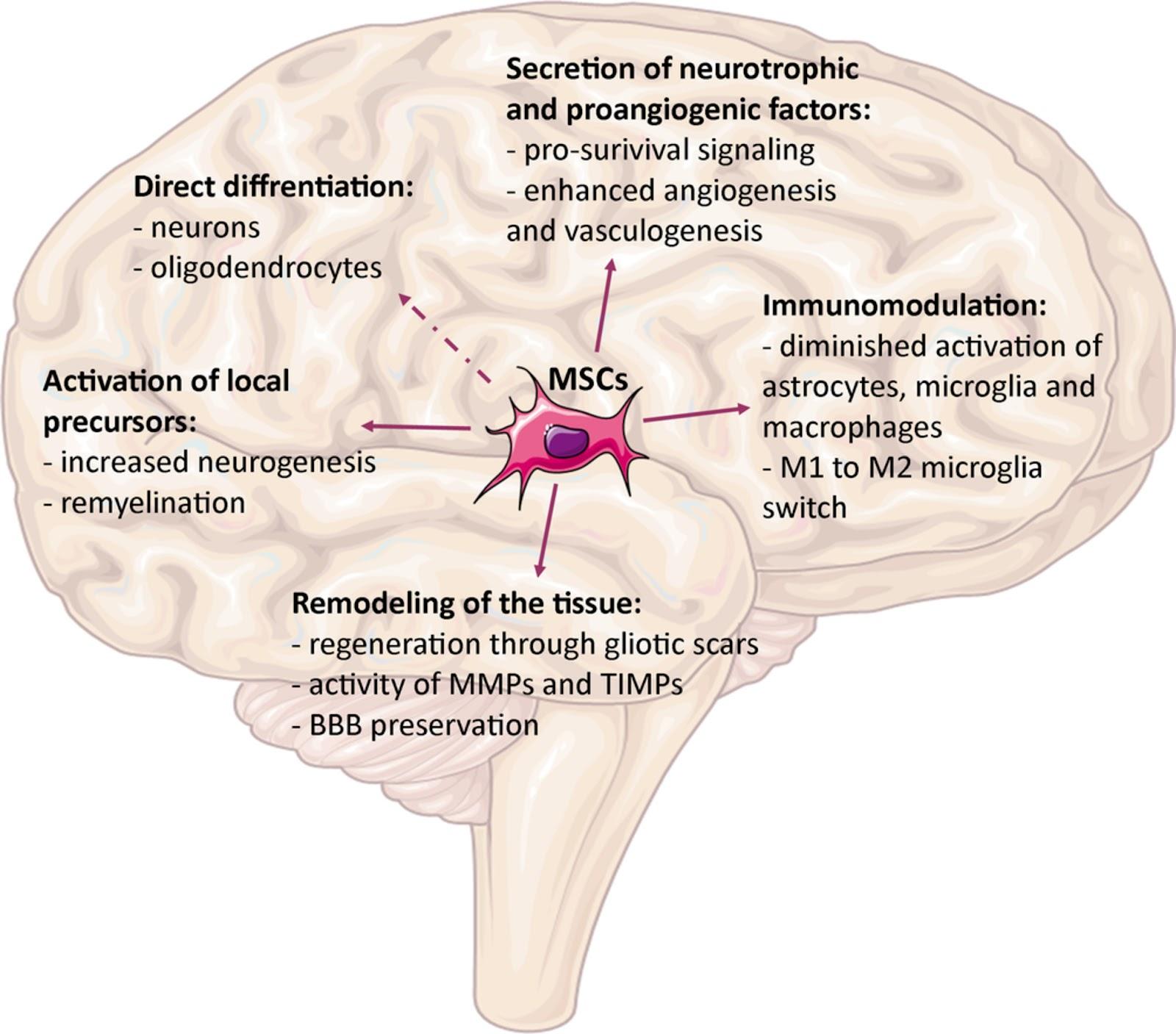
MSCs or mesenchymal stem cells are known as multipotent stem cells with self-renewal and differentiation ability. Among other stem cells, these have the greatest proliferation rate, meaning their efficiency rate can be much higher than the rest.
Stem cell research for autism indicates mesenchymal stem cells to be most effective against underlying autism symptoms, like inflammation and immune dysfunction. These cells secrete growth factors, cytokines, and chemokines that help repair damaged cells and tissues to their healthy form.
MSCs specifically derived from umbilical cord tissue are highly immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory in nature. They are also immune-privileged cells, with no risk of rejection within the body.
Induced pluripotent stem cells
iPS are lab-engineered tissue-specific stem cells that behave like embryonic stem cells but differ in some ways. These stem cells are largely used for testing and developing drugs and therapies.
Clinical trials with stem cells that support autism treatment
Most research and stem cell therapy for autism clinical trials started with the treatment of cerebral palsy. Like cerebral palsy, autism is a heterogeneous neurodevelopmental disorder, that involves inflammation and immune dysfunction both of which can be treated by stem cells particularly.
According to recent research, mesenchymal cells, or MSCs make the most promising stem cell therapy option for autism for their low immunogenicity and immune modulation functions. MCSs possess the incredible ability to promote inflammation to an under-activated immune system and restrain inflammation when the immune system is over-activated to prevent self-destruction.
According to the US National Institute of Health official database, 493 MSC-based clinical trials have been carried out that prove the biomedical potential of MSCs in treating, inflammatory, neurological, and autoimmune diseases like cerebral palsy, Alzheimer’s, autism, multiple sclerosis, leukemia, and Parkinson’s disease, etc.
Conclusion
Stem cell discovery has led to promising treatment development for autism. Their regenerative capabilities have made previously incurable neurological and developmental disorders manageable. Stem cell therapy along with other interventions can produce effective and lasting results by substantially increasing the chances of living an independent life for a person with autism.













